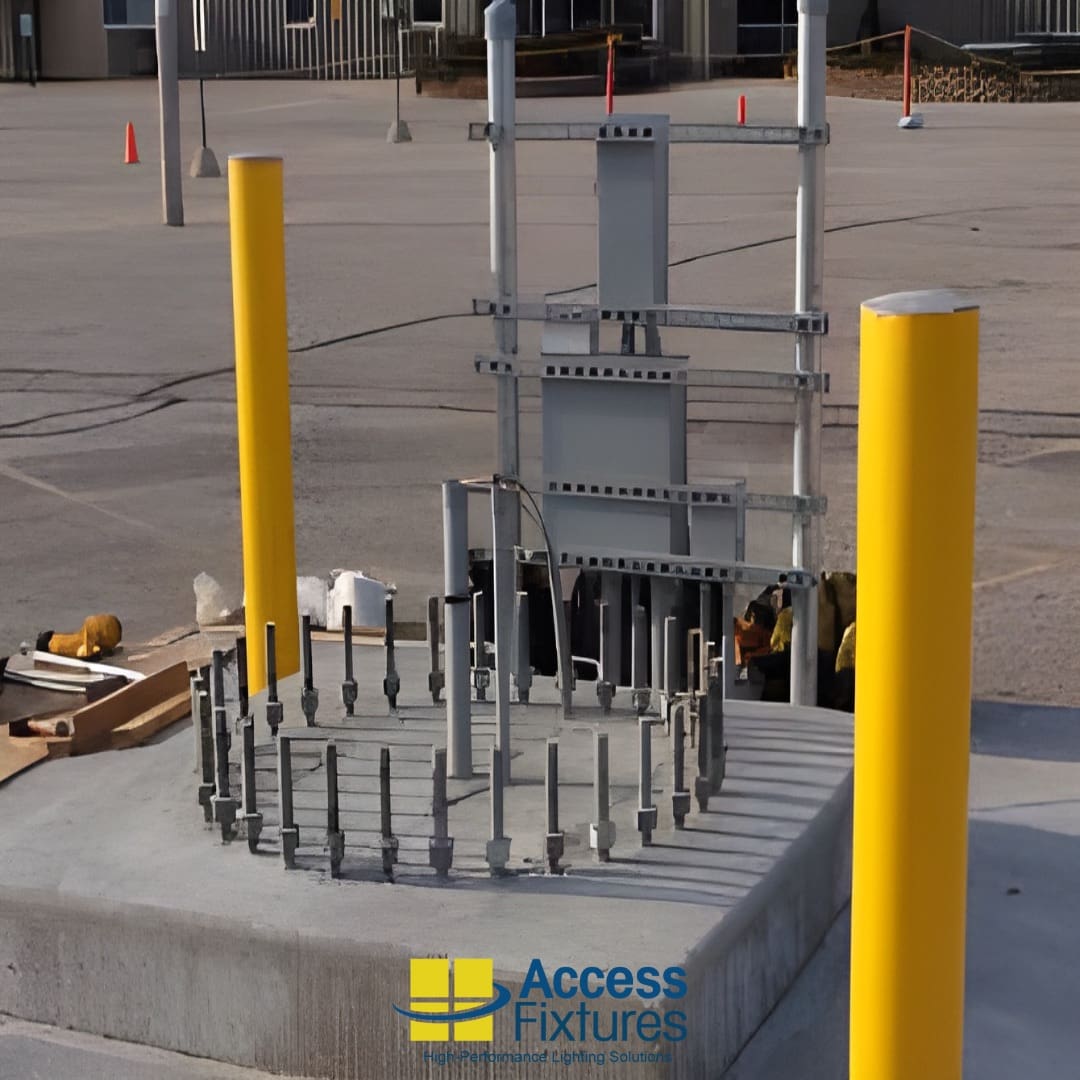
When planning an outdoor lighting project, selecting the right pole type is crucial to ensuring the durability, performance, and longevity of your system. Two primary options are bolt-down steel poles and direct burial composite poles, each offers specific advantages based on environmental conditions, installation requirements, and long-term maintenance needs. Understanding these differences and knowing how to install a light pole will help you make the most suitable choice for your project.
A critical aspect of the installation process is the bolt pattern, which ensures proper alignment and stability of the light poles. Using a bolt pattern template can facilitate accurate positioning, which is essential for the safety and stability of the installation.
Considering the light pole cost is essential when choosing between bolt-down steel poles and direct burial composite poles, as each option has different price implications based on installation methods and materials.
Here is an examination of the key differences between these two types of poles, focusing on installation methods, material characteristics, and real-world applications, and providing a comparison of their advantages and drawbacks.
Key Takeaways
-
-
Installation and Stability: Bolt-down steel poles provide superior stability but require a concrete foundation, while direct burial composite poles are quicker and cheaper to install.
-
Material Suitability: Steel poles are strong and ideal for heavy-duty use, but need anti-corrosion treatments in coastal areas. Composite poles resist corrosion naturally, making them better for coastal environments.
-
Maintenance and Costs: Bolt-down steel poles are easier to maintain and replace, while composite poles require less upkeep but are harder to replace once buried.
-
Planning and Preparation
Proper planning and preparation are crucial for a successful light pole installation project. This stage involves understanding the site conditions, obtaining necessary permits, and selecting the right light pole for the job. It is also important to plan for the electrical installation and hire a qualified electrician to ensure compliance with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local regulations. By laying a solid foundation during the planning phase, you can ensure a smoother installation process and a more durable lighting system.
Understanding Ground Conditions
Understanding the ground conditions is essential for determining the appropriate foundation and installation method. The type of soil, its stability, and bearing capacity can significantly affect the installation process. Conducting a thorough soil analysis can provide valuable insights into the site conditions, helping to identify potential issues and determine the best course of action.
When planning for an embedded installation, it is important to consider soil conditions and material choices like aluminum and fiberglass to prevent rust. Consulting with an engineer can also be beneficial for both embedded and anchored pole installations.
Factors to consider when assessing ground conditions include:
-
Soil Type and Stability: Different soils have varying levels of stability and bearing capacity. For instance, sandy soils may require deeper burial for direct burial poles to ensure stability.
-
Bearing Capacity: The soil’s ability to support the weight of the light pole and fixtures is crucial. Weak soils may necessitate additional reinforcement or a different installation method.
-
Potential Issues: Be aware of potential problems such as waterlogging, erosion, or soil movement, which can affect the stability of the light pole.
-
Environmental Factors: Consider wind loads, seismic activity, and other environmental factors that could impact the installation process.
By thoroughly understanding the ground conditions, you can choose the most suitable installation method and ensure a stable, long-lasting light pole installation.
Obtaining Permits and Meeting Regulations
Before commencing any light pole installation project, it’s essential to obtain the necessary permits and comply with local regulations. This includes ensuring adherence to safety codes, electrical requirements, and setback regulations. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, penalties, and project delays.
Factors to consider when obtaining permits include:
- Safety Codes and Standards: Ensure that your installation meets all relevant safety codes and standards to protect both workers and the public.
- Electrical Requirements: Comply with local electrical regulations to ensure the safe and efficient operation of your lighting system.
- Setback Regulations and Zoning Laws: Adhere to setback regulations and zoning laws to avoid legal issues and ensure proper placement of your light poles.
- Environmental Regulations: Obtain any necessary environmental permits, especially if your project is in a sensitive area or involves significant ground disturbance.
By obtaining the necessary permits and meeting all regulatory requirements, you can avoid legal complications and ensure a smooth, compliant installation process.
Importance of a Secure and Solid Light Pole Installation
A secure and solid light pole installation is crucial for ensuring the safety and longevity of your lighting system. Properly installed light poles can withstand various environmental conditions, such as strong winds, heavy rainfall, and extreme temperatures, thereby reducing the risk of accidents and damage.
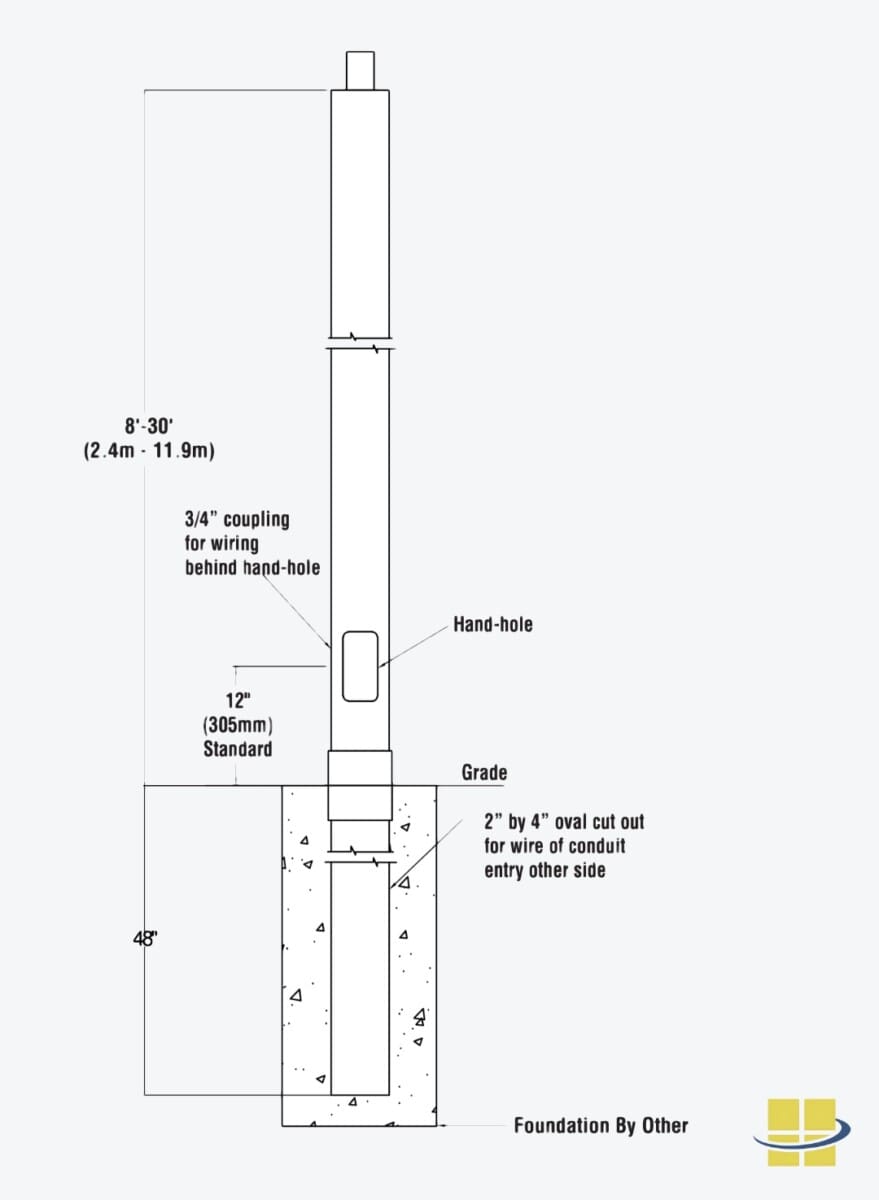
One of the most critical components of a secure light pole installation is the use of anchor bolts. These bolts are specifically designed to secure the pole to the concrete foundation, providing a strong and stable base. Correct installation of anchor bolts is essential to prevent the pole from toppling over or becoming loose over time.
In addition to anchor bolts, a solid concrete foundation is vital. The foundation should be designed and poured according to the manufacturer’s specifications, taking into account factors such as soil type, wind load, and the weight of the pole. A well-designed concrete foundation can withstand various loads and stresses, ensuring the stability and safety of the lighting system.
The importance of a secure and solid light pole installation cannot be overstated. A poorly installed light pole can lead to a range of problems, including:
- Accidents and Injuries: A loose or toppling light pole can cause accidents and injuries to people and vehicles.
- Damage to Property: A falling light pole can damage surrounding property, including buildings, vehicles, and landscaping.
- Electrical Hazards: A poorly installed light pole can create electrical hazards, including shock and electrocution.
- Maintenance Costs: A poorly installed light pole can require frequent maintenance and repairs, leading to increased costs and downtime.
In contrast, a secure and solid light pole installation can provide numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Safety: A well-installed light pole can reduce the risk of accidents and injuries.
- Increased Longevity: A secure light pole installation can extend the lifespan of the lighting system.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: A well-designed and installed light pole can minimize maintenance and repair costs.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: A secure and solid light pole installation can improve the appearance of the surrounding area.
In conclusion, a secure and solid light pole installation is essential for ensuring the safety, longevity, and aesthetics of your lighting system. By using anchor bolts, designing a solid concrete foundation, and following proper installation procedures, lighting contractors and installation workers can provide a reliable and efficient lighting system that meets the needs of various applications.
Light Pole Installation Methods: Bolt Down vs. Direct Burial Poles
The installation process has a significant impact on the stability and cost of your project. Understanding how each method works will help you determine the best solution for your lighting needs. Understanding the light pole installation cost associated with each method will help you budget effectively for your project.
Bolt Down Poles
Bolt-down poles are mounted onto a pre-poured concrete foundation with embedded anchor bolts. The pole is then secured to the base with washers and nuts, creating a firm, long-lasting connection. Ensuring the correct installation of each anchor bolt is crucial for the stability and longevity of bolt-down poles.
Typical Applications:
-
Parking lots
-
Sports fields
-
Urban streets
-
Industrial areas
These poles are ideal in high-traffic or wind-exposed locations where structural stability is essential.
Advantages:
-
Superior Stability: The concrete foundation offers exceptional stability, even in harsh weather conditions.
-
Easy Replacement: If the pole needs replacing, the foundation stays intact, allowing the new pole to be easily mounted onto the existing base.
-
Supports Heavier Fixtures: Bolt down poles are ideal for larger, heavier lighting fixtures, such as those used in sports facilities.
Drawbacks:
-
Higher Installation Costs: The concrete foundation adds material and labor costs, extending project timelines due to the curing period.
-
Complex Installation: Installation requires more planning, heavy equipment, and additional time compared to direct burial methods.
Direct Burial Poles
Direct burial poles are installed using the direct burial method by placing the pole base directly into a pre-dug hole, then backfilling the hole with compacted soil, gravel, or concrete for stabilization. No concrete foundation is required.
To ensure stability and proper installation, it is recommended to use a concrete mixture for filling holes when direct burying light poles.
Typical Applications:
-
Parks and recreational areas
-
Rural roads and pathways
-
Coastal and saltwater environments
These poles are preferred for areas where corrosion resistance and quick, cost-effective installation are essential.
Advantages:
-
Faster Installation: Without the need for a concrete foundation, the installation process is quicker and less labor-intensive.
-
Lower Costs: Fewer materials are required, which leads to significant savings in both labor and installation.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Composite direct burial poles resist corrosion, making them ideal for coastal and high-moisture environments.
Drawbacks:
-
Harder to Replace: Once installed, replacing direct burial poles can be costly and labor-intensive since they require excavation.
-
Reduced Stability: In softer soils or regions prone to ground shifts, direct burial poles may not offer the same stability as those mounted on concrete foundations.
Choosing the Right Light Pole
Selecting the right light pole for the job is critical for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. There are various types of light poles available, each with its unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision that best suits your project’s needs. Considering the light pole installation cost is also crucial when selecting the right type of pole for your project.
Types of Light Poles
When planning your outdoor lighting project, it’s essential to consider the different types of light poles available. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the specific needs of your project. For instance, solar light poles are an eco-friendly option that can save on energy costs, while traditional AC-powered light poles might offer more consistent performance in areas with less sunlight.
Each type of light pole comes with its own light pole installation cost, which should be considered when planning your project.
Common types of light poles include:
- Steel Poles: Known for their durability and strength, steel poles are ideal for urban and industrial areas. However, they are prone to rust and corrosion, especially in coastal environments, unless treated with anti-corrosive coatings.
- Aluminum Poles: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum poles are suitable for coastal and high-moisture environments. However, they may not be the best choice for high-wind areas due to their lower strength compared to steel. For direct burial installations, recommended pole materials include aluminum and fiberglass due to their rust-resistant properties.
- Fiberglass Poles: These poles are durable and low-maintenance, making them ideal for parks and recreational areas. However, they may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Factors to consider when selecting a light pole include:
- Strength and Durability: Choose a pole that can withstand the environmental conditions and support the weight of the fixtures.
- Aesthetic Appeal and Design: Consider the visual impact of the pole and how it fits with the surrounding environment.
- Environmental Factors: Take into account wind loads, corrosion resistance, and other environmental factors that could affect the pole’s performance.
- Budget and Cost-Effectiveness: Balance the initial cost of the pole with its long-term maintenance and replacement costs.
By carefully planning and preparing for the light pole installation project, selecting the right light pole, and obtaining necessary permits, you can ensure a successful and safe installation that meets your specific needs and requirements.
Material Types: Steel vs. Composite Light Poles
Steel Poles
Ideal For:
-
Urban and industrial areas
-
High-wind and high-traffic zones
-
Heavy-duty applications (e.g., large-scale lighting)
Advantages:
-
High Strength: Steel poles offer superior strength, making them ideal for supporting large fixtures and withstanding high winds.
-
Customizability: Steel poles can be manufactured to specific heights and strengths, offering flexibility in design.
-
Long Lifespan: With the right coatings (e.g., galvanization), steel poles can last for decades.
Drawbacks:
-
Corrosion Risk: Steel is prone to rust in coastal areas unless protected with anti-corrosive coatings, which can increase costs.
-
Example: In Santa Monica, steel poles required special coatings to resist saltwater corrosion.
-
Heavier and More Expensive to Install: The weight of steel poles necessitates more labor, equipment, and cost to transport and install. The light pole installation cost for steel poles can be higher due to the need for anti-corrosive treatments and heavier installation equipment.
Composite Poles
Ideal For:
- Coastal and corrosive environments
- Parks and recreational areas
- Solar lighting projects
Advantages:
- Corrosion Resistance: Composite poles are naturally resistant to rust, making them ideal for coastal or high-moisture locations.
- Example: In Florida Keys, composite poles were chosen for their ability to resist saltwater corrosion.
- Lightweight: These poles are much lighter than steel, reducing labor and transport costs.
- Low Maintenance: Unlike steel, composite poles do not need coatings or frequent maintenance, making them easier to care for in the long term.
- Cost-Effective: The light pole installation cost for composite poles is generally lower due to their lightweight nature and corrosion resistance.
Drawbacks:
- Limited Strength: Composite poles do not offer the same load-bearing capacity as steel, making them unsuitable for heavy fixtures or high-wind areas.
- Less Stability in Soft Soils: Composite poles may require additional engineering in softer or shifting soils to ensure they remain securely anchored.
Considering Sand, Saltwater, and Structural Engineering Before Installing
Sandy Environments
In areas like Santa Monica, sandy soil requires deeper burial for direct burial poles to ensure stability. Having a longer light pole shaft is crucial for maintaining stability in such environments. Poles should be buried at a depth of 10% of the pole’s height plus 3 feet. For example, a 30-foot pole should be buried at least 6 feet deep to prevent shifting. Additionally, using gravel or concrete backfill helps secure the pole in loose sand, which is essential for areas prone to high winds.
A hand hole is important for guiding wires and securing the pole during installation to prevent accidents. It serves as an access point used for rigging purposes when lifting the pole, ensuring proper balance and stability.
Coastal and Saltwater Areas
In coastal regions such as the Florida Keys, composite poles are often favored due to their natural resistance to corrosion. Unlike steel, composite poles don’t require costly anti-corrosion coatings or frequent maintenance. If using steel poles, they must be treated with corrosion-resistant coatings like galvanization to withstand salt exposure, but these treatments will still need periodic maintenance over time.
Wind Load Considerations
High-wind areas, common in both sandy and coastal environments, require poles with higher wind load capacity. Bolt down steel poles offer superior stability in such conditions due to their secure foundation and structural strength. Direct burial poles in high-wind zones need deeper burial and, in some cases, extra anchoring to ensure they remain secure.
Structural Engineering
For challenging environments, structural engineering is essential to ensure proper installation. Engineers can assess:
-
Pole depth and backfill requirements based on soil conditions and wind loads.
-
Load-bearing capacity to ensure poles can support fixtures in high-wind or high-traffic areas.
-
Corrosion protection strategies to determine if steel poles with coatings or composite poles are the better option.
Hydraulic rotary equipment plays a crucial role in the installation process of helical foundations, as it is essential for driving a steel anchor into the ground effectively. This equipment is significant in efficient construction techniques.
By accounting for these factors, you can ensure a stable, long-lasting installation that minimizes risks and maintenance costs over time.
Comparison Table: Bolt Down Steel Poles vs. Direct Burial Composite Poles
| Pole Type | Bolt Down Steel Poles | Direct Burial Composite Poles |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Method | Requires concrete foundation and anchor bolts | Buried directly into the ground |
| Installation Cost | Higher due to foundation and labor costs | Lower, no need for a concrete foundation |
| Installation Time | Longer due to foundation curing | Faster, no foundation required |
| Replacement | Easy to replace with minimal disruption | Harder and costlier to replace once buried |
| Corrosion Resistance | Requires special coatings in coastal areas | Naturally corrosion-resistant |
| Stability | High stability for large fixtures | Adequate but may shift in soft soils |
| Ideal Environment | Urban, industrial, high-traffic areas | Coastal, rural, and high-moisture environments |
| Weight | Heavy, requires more labor and equipment | Lightweight, easier to transport |
| Lifespan | Long-lasting with regular maintenance | Long-lasting with minimal maintenance |
| Light Pole Installation Cost | Higher for bolt down steel poles due to foundation and labor costs | Lower for direct burial composite poles due to quicker installation and fewer materials required |
Conclusion
Choosing between bolt down steel poles and direct burial composite poles ultimately depends on your project’s specific needs, environmental conditions, and long-term maintenance considerations.
- Bolt down steel poles are the ideal choice for urban, industrial, or high-traffic environments where stability and the ability to support heavy fixtures are crucial. While they require higher upfront installation costs due to the concrete foundation, their durability and ease of replacement make them a reliable, long-term solution.
- Direct burial composite poles, on the other hand, are best suited for coastal or rural environments where corrosion resistance and quick installation are key. They offer a cost-effective, low-maintenance alternative, especially in areas exposed to saltwater or moisture, though they may lack the structural strength needed for larger fixtures or high-wind zones.
By carefully assessing factors like soil type, wind load, and corrosion risks, and possibly consulting with a structural engineer, you can make an informed decision that ensures your outdoor lighting system performs reliably for years to come. Considering the light pole installation cost is crucial for making an informed decision that balances budget and performance. For expert advice or tailored recommendations, reach out to our lighting specialists—we’re here to help guide you to the best solution for your project’s unique requirements.


